Vision¶
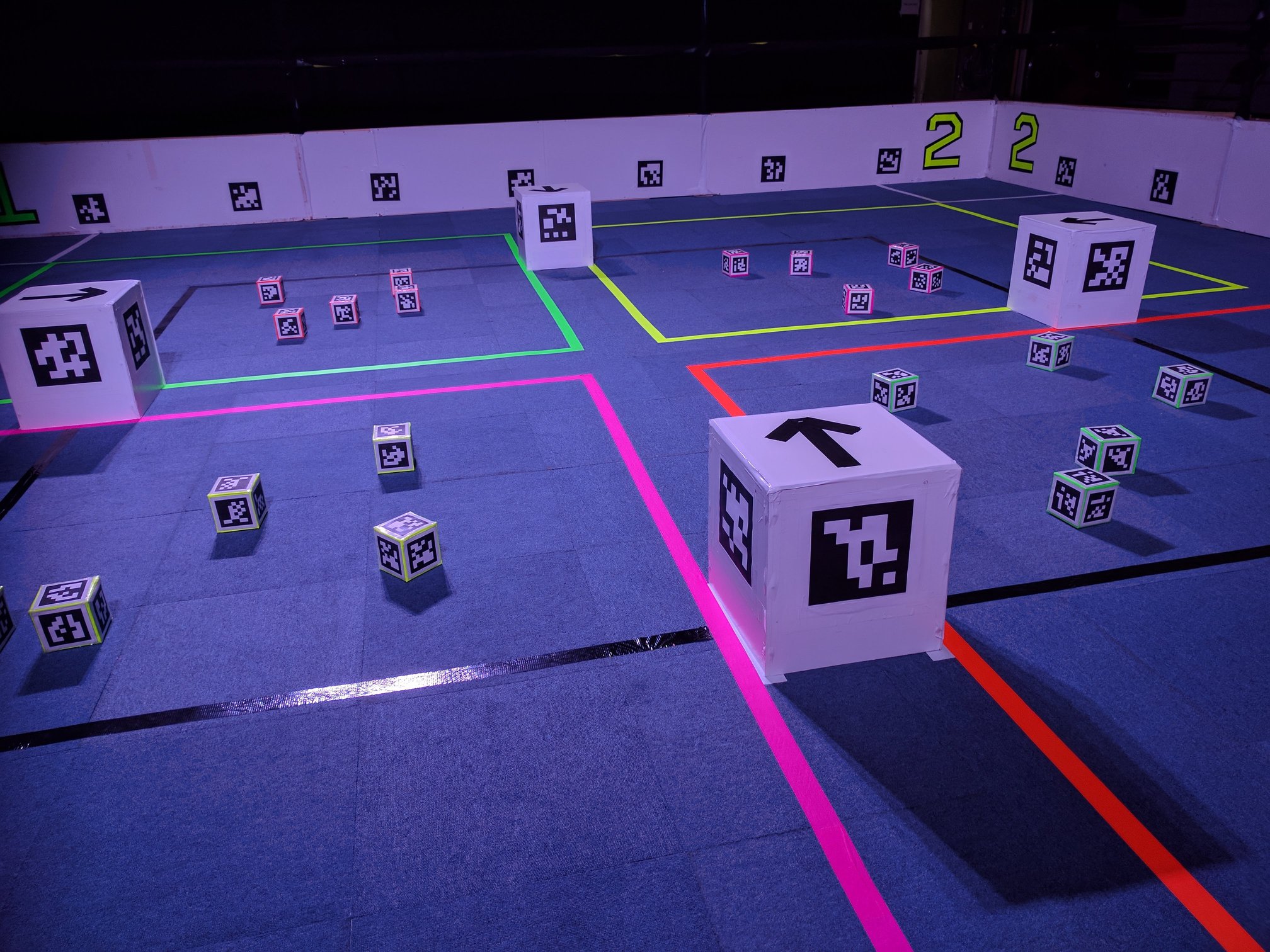
Your robot is able to use a webcam to detect Fiducial Markers.
Specifically it will detect AprilTags, using the 36H11 marker set.
Using Pose Estimation, it can calculate the orientation and position of the marker relative to the webcam. Using this data, it is possible to determine the location of your robot and other objects around it.
You can download the markers from the resources page.
Searching for markers¶
Assuming you have a webcam connected, you can use robot.camera.see() to take a picture. The software will process the picture
and returns a list of the markers it sees.
markers = robot.camera.see()
Tip
Taking images while moving will cause them to be blurry, which will cause marker detection to fail. Try pausing movement while taking an image.
Saving camera output¶
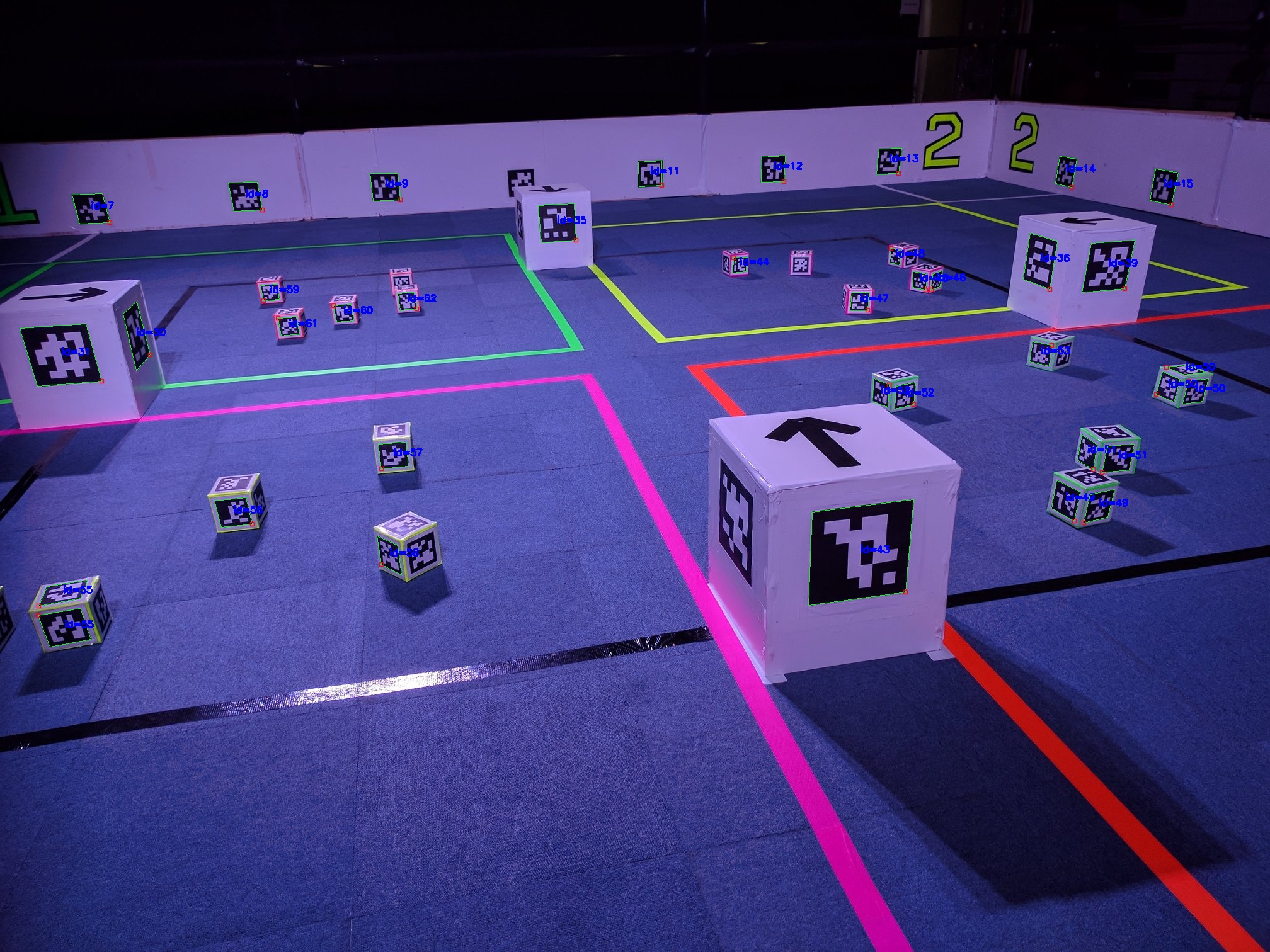
You can also save a snapshot of what your webcam is currently seeing. This can be useful to debug your code. Every marker that your robot can see will have a square annotated around it, with a red dot indicating the bottom right corner of the marker. The ID of every marker is also written next to it.
Snapshots are saved to your USB drive, and can be viewed on another computer.
robot.camera.save("snapshot.jpg")
Markers¶
The marker objects in the list expose data that may be useful to your robot.
Marker ID¶
Every marker has a numeric identifier that can be used to determine what object it represents.
markers = robot.camera.see()
for m in markers:
print(m.id)
Position¶
Each marker has a position in 3D space, relative to your webcam.
You can access the position using m.distance, m.azimuth and m.elevation.
markers = robot.camera.see()
for m in markers:
print(m.distance) # Distance to the marker from the webcam, in millimetres
print(m.azimuth) # Bearing to the marker from the webcam, in radians
Azimuth is the angle in radians to the right from the center of the camera to the center of the marker.
Elevation is the angle in radians above the center of the camera to the center of the marker.
It is also possible to look at the Orientation of the marker.
Tip
You can use the math.degrees function to convert from radians to degrees.
Size¶
Markers can come in different sizes.
You can access the size of a marker using m.size.
Check the rules to find out how big the different marker types are.
markers = robot.camera.see()
for m in markers:
print(m.size)
Pixel Positions¶
The positions of various points on the marker within the image are exposed over the API. This is useful if you would like to perform your own Computer Vision calculations.
Pixels are counted from the origin of the image, which conventionally is in the top left corner of the image.
markers = robot.camera.see()
for m in markers:
print(m.pixel_corners) # Pixel positions of the marker corners within the image.
print(m.pixel_centre) # Pixel positions of the centre of the marker within the image.